Biodegradable hydrogels for microrobots
If micro and nanorobotics are to be used for future biomedical applications such has diagnostics and targeted drug delivery, these small-scale robots must be both biocompatible and biodegradable. Micro and nanorobots fabricated with non-cytotoxic, biodegradable soft components suitable for use in clinical applications, will ensure improved device assimilation, optimal tissue interaction and minimized immune reactions.
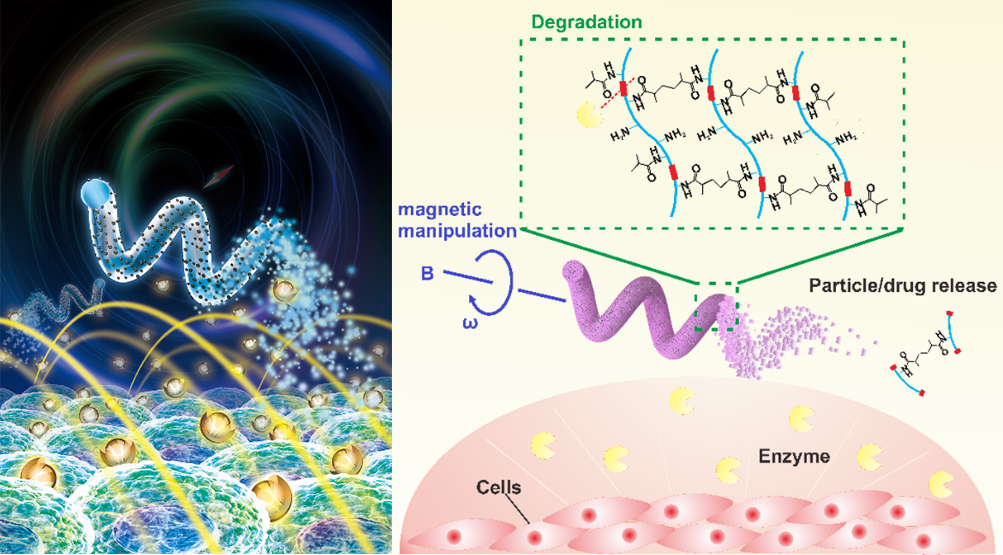
Our research into the fabrication of biodegradable microrobots using gelatine methacryloyl (GeIMA) has resulted in a magnetically driven, helical structured microswimmer. Tests have shown that these microrobots can be gradually digested by cell-released enzymes in cell cultures. These non-cytotoxic, biodegradable hydrogel microswimmers will greatly advance the use of microrobots in medicine by eliminating the need for retrieval from the body once their task has been completed.
Contacts: Xiaopu Wang
References:
Xiaopu Wang, Xiao‐Hua Qin, Chengzhi Hu, Anastasia Terzopoulou, Xiang‐Zhong Chen, Tian‐Yun Huang, Katharina Maniura‐Weber, Salvador Pané, and Bradley J. Nelson. “3D Printed Enzymatically Biodegradable Soft Helical Microswimmers.” Advanced Functional Materials 2018, 28, 1804107.